Brain injury key facts & figures
Brain injury key facts and figures
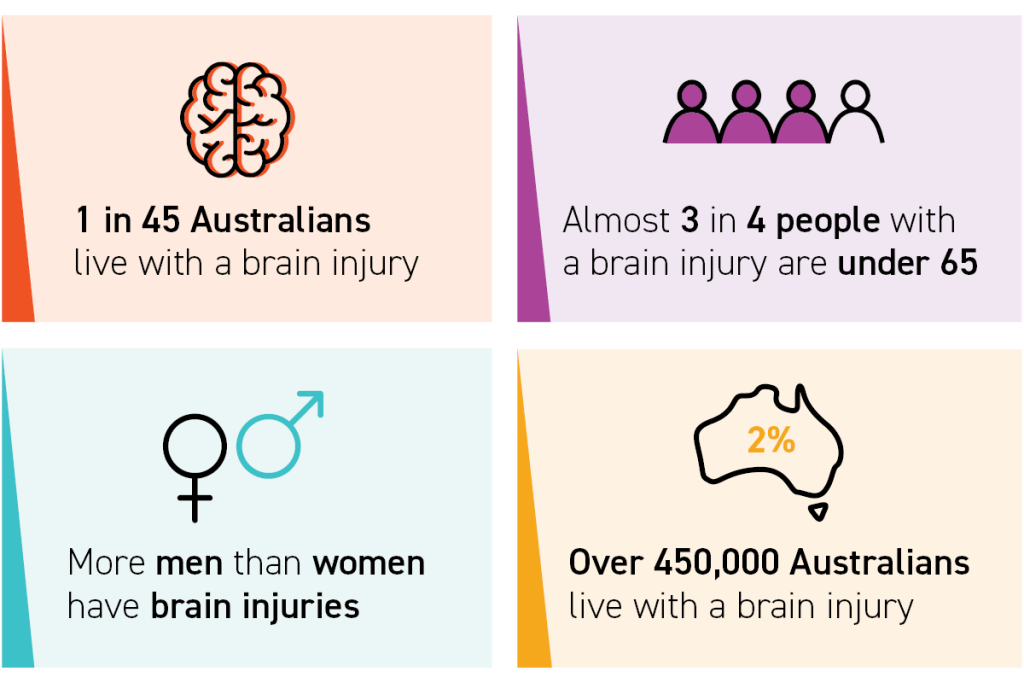
- 1 in 45 Australians live with a brain injury. (AIHW, 2007)
- Every 4 minutes, someone in Australia is hospitalised for a head injury. (AIHW, 2021)
- More men have brain injuries than women. (AIHW, 2007)
- Almost 3 out of 4 people with a brain injury are under 65. (AIHW, 2007)
- 1 in 4 brain injury hospitalisations are people aged 15 – 24. (AIHW, 2021a)
- More than 450,000 Australians have a brain injury. (AIHW, 2023